What is Restaurant Profit Margin and How to Improve it? Your Ultimate Guide
Just like any other business, the aim of running a restaurant is also to earn profits. During the opening of a restaurant, the goal of each restaurateur might differ. But the operations will always be focused on profit-making. No profit means no money and no money eventually means no restaurant. The only means to business survival is earning a high profit margin.
The average restaurant profit margin is unfortunately very low, a meagre 3% to 7%. This is due to high labor costs, employee turnover, workforce shortages, raw material costs and higher competition.

Ever since the onset of the pandemic, the profit margin has only reduced further forcing restaurants to struggle in making ends meet. Therefore, understanding the profit margin, keeping track of it and making earnest efforts to keep it as high as possible is an inevitable responsibility of every restaurant owner or manager.

As the one responsible for the success of the restaurant, it is essential for you to understand the factors that affect the profit margin and the ways in which you can improve it. We are not here to startle you with data about low profit margins. Well, if you are looking to boost your restaurant’s bottom line or simply wish to better understand how it works, this blog has been curated for you. After reading this blog, you will know how to combat the problem of low profit margins and start growing profits for the restaurant to thrive.
It is nothing but the amount that stays in hand after the restaurant has completed the payment for all its expenses. This profit margin reveals the ability of the restaurant to convert its sales into profits.
Profit margin is usually measured in two ways: gross profit margin and net profit margin.
Gross Profit Margin
This calculation shows the profits attained by deducting the food and beverage sales with the direct costs associated with those sales, also known as Cost Of Goods Sold (COGS). COGS refers to the direct costs of producing the goods sold by the restaurant. This includes raw material cost, ingredient cost and other direct expenses that are associated with the food and beverage production. Knowing how much this gross profit margin is helps the restaurant improve the efficiency of the core food and beverage operations.
Net Profit Margin
Unlike Gross Profit Margin that takes into account only the direct costs of goods sold, net profit margin includes all expenses like COGS, operating expenses, taxes, interest, labor and other possible costs. It calculates the profitability ratio of the business, that is, how much revenue has been earned versus how must cost has been incurred to generate that revenue. Net profit margin is a more holistic approach to the restaurant’s profitability. It is essential for assessing the overall financial wellness and long-term stability of the business.

Data Collection
Before calculating the restaurant’s profit margins, one needs to have certain data at their disposal. Due to this, having a POS system to keep track of restaurant sales data becomes mandatory. Undertaking this process manually will lead to several human errors and provide only incorrect profit margin calculations.
The main data types are:
- Cost Of Goods Sold
- Total Revenue
- Sales Revenue
- Expenses
- Gains & Losses
Why Is Restaurant Profit Margin Important?
Both gross profit margin and net profit margin are complementary metrics that provide valuable insights into the business’ sales, expenses, revenue and profits.
A good gross profit margin indicates efficiency in core restaurant operations. Still, if there are excessive operating expenses that ruin the net profit, even a restaurant with a strong gross profit margin will struggle to make ends meet.
A healthy net profit margin shows that the restaurant is effectively managing all its costs and is successfully reaping profits across all aspects of the business.
Both the metrics should be monitored and analyzed regularly to get a wholesome understanding of the business’ performance.
What Is A Good Profit Margin For Restaurants?
While this question lingers in the minds of many restaurateurs, the truth is that there is no such thing as a good average profit margin for restaurants. The fact is that what is considered a good margin for one restaurant need not necessarily be good for another one. It relies on the ratio between the operating and overhead expenses to the total income.
Profit margins will definitely vary between every restaurant. However, restaurants that function in the same category share a typical and similar average profit margin range. Here is a quick look at how profit margins vary between restaurant types.
1) Full-Service Restaurants (FSRs)
Any restaurant that has staff, servers, bartenders, a host and kitchen staff is known as a Full-Service Restaurant. Due to higher expenses when compared to other types of restaurants, FSRs get only a low profit margin on average. The items on their menu are also priced high as they have to meet their labor costs, overhead costs and other operating expenses. Taking all these factors into consideration, FSRs usually enjoy profit margins between 3% to 5%.
2) Quick-Service Restaurants (QSRs)
Such restaurants have high profit margins – between 6% and 9%. But exceptions do exist as well. This is because they have less staff, higher sales volume, cheaper ingredients, etc. Since fast food restaurants are entering into the online ordering and delivery domain as well, they are also facing additional expenses these days.
3) Food trucks
Operating a food truck brings with it a completely new set of expenses like fuel, specialized licenses and permits, etc. Food trucks are becoming increasingly popular as they are use high-quality ingredients to serve gourmet dishes in an unassuming environment. Although the overhead costs are low, they spend quite an amount on expensive ingredients. This brings their average profit margin to something between 6% and 9%.
4) Cloud Kitchens And Catering
Since they require very few staff and need no brick-and-mortar outlet to serve customers, they spend only a little amount on overhead costs. Although they would incur the same expenses while purchasing ingredients, they do not have to spend exorbitant amounts on rent. Their staff costs are low, they do not need to spend anything on interior decoration or renovation, their furnishing costs are almost nil, they need to arrange or pay for parking spaces and so on. This leads to a drastic increase of their profit margins.
Strategies To Improve Restaurant Profit Margin
When profit margins begin to decrease, the restaurant management will first engage in cost-cutting exercises. But such activities can be self-destructive. You could instead follow these strategies to improve the restaurant's profit margin.
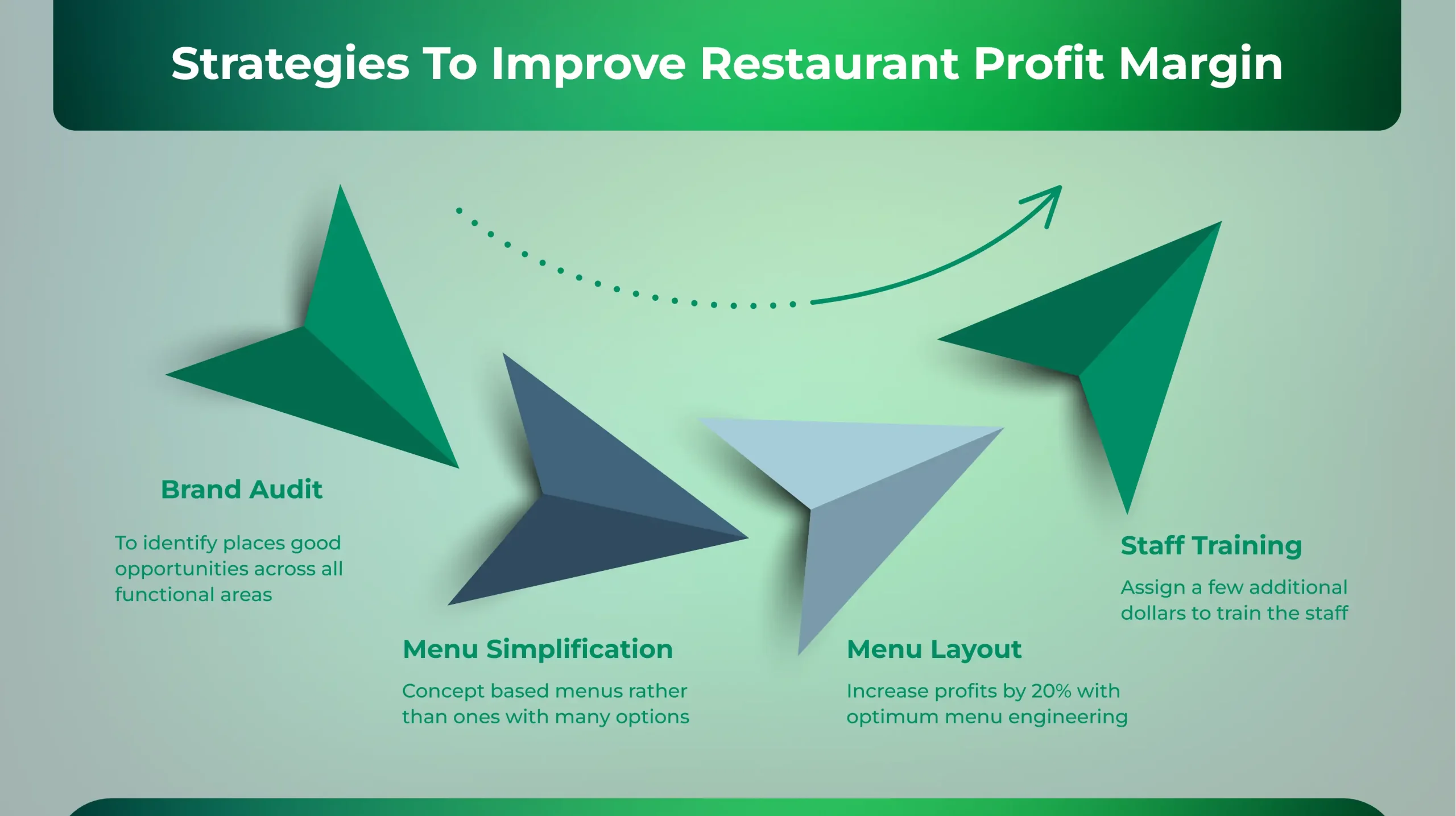
1) Brand Audit
An extensive brand audit helps to identify places that offer good opportunities for restaurants across all functional areas. This is a better approach than simply focusing on ways to decrease expenses. This will boost revenue and streamline operations that, in turn, produce long-term sustainability and growth irrespective of the market conditions.
2) Menu Simplification
Concept based menus yield better results than the ones that offer many options. With too many menu offerings, the back-of-house operations only get complicated and additional labor becomes necessary. While engaging in menu engineering exercises, optimizing the price of the items is essential. With careful analysis of the profitability of the items and factors that are influencing guest decisions, the management will be able to take better decisions about retaining and removing menu items.
3) Menu Layout
It is important to be intentional about the menu layout. Menu engineering is not just a science, but an art as well. The layout of the written menu, digital menu and drive-thru menu should lay emphasis on the most profitable items. With optimum engineering of the menu, the profits can be increased by 20%
4) Staff Training
Do not hesitate to assign a few additional dollars to train the staff. When the employees are excited, it automatically gets transferred to the customers as well.
5) Marketing Along with PR
Do not stop with marketing. Execute some Public Relations campaign too. You can build robust relations with the media through public relations activities. This will help in creating a positive public awareness and generate implied endorsements. This weaves a story around the restaurant assisting in brand recognition and buzz.
6) Smooth Operations
By streamlining the front and back-of-house, the restaurant benefits to a great extent. Table turnover can be made quicker, and more customers served, when the front and back house is equipped with tools to work smarter. Also incorporate technology like self-ordering and payment through QR codes to complete the order process for time-conscious customers.
7) Monitor The KPIs
Without proper metrics, management is impossible. You must track the most important KPIs in real time. You must know the kitchen capacity and get information in real time about whether you will be under or over-staffed in the upcoming work hours. Monitoring the right KPIs in real time will help anticipate problems and solve it and not wait till the month end to have a look at the profit margin.
8) Technology For Labor Scheduling
Streamlining the staff schedules is key to a perfectly staffed restaurant. Although it seems to be an easy task, managing employees requires a lot of attention to detail. Today, many tools are available to schedule staff in a smart manner allowing them to even exchange shifts between each other without the need for a manager’s intervention.
9) Strong Online Presence
List the restaurant in Google with updated information about working hours, address, menu and all other vital information. Make it easy for customers to place online orders. Make constant use of the restaurant’s social media platforms including Instagram, Facebook and Twitter, keeping them updated with the latest news, discounts and offers.
10) Inventory Management
Use ingredients effectively. Reduce food waste by employing strategies of inventory management and demand forecasting. This is very important for improving profit margins as food constitutes almost a third of the restaurant’s total expenses.
11) Top-Line Growth
Restaurant industry experts know very well that top-line growth cures bottom-line ailments. The things that require attention are:
- Creating regular customers through good guest experience, loyalty programs and constant menu innovation
- Bringing in new guests through marketing, advertising and promotional activities
- Increase the average check size by providing add-ons, sizes and shareables
- Improving sales channels by offering door delivery and off-premises options
- Modifying product lines by catering to the needs of vegetarians as well
- Offering merchandize products if possible

Restaurant Profit Margins: A Delicate Balance
Having read this blog, you would have now realized that there are multiple ways to increase profit margins of restaurants. All you need to do is to closely inspect the establishment’s unique needs and situation and determine which of the above strategies works in your favor.
Find ways to lower expenses without compromising on customer experience. Analyze sales channels and see if any way to increase the overall revenue exists. For further assistance in digital marketing for restaurants, get in touch.